Slide DMS173 [Ovarian follicles. monkey, PTS]. This thin section shows well the general features of the ovary. Identify the surface ("germinal") epithelium, tunica albuginea, hilus, cortex, and medulla. Note that the surface epithelium is continuous with the mesothelium of the mesovarium. Follow the branches of the ovarian artery as they extend from the hilus, through the medulla and into the cortex. Compare the stroma of the medulla with that of the cortex. The cortical stroma consists of whorls of densely packed fibroblast-like cells. The medullary stroma is more like loose fibroelastic connective tissue with some smooth muscles cells.
Look for examples of each of the following types of ovarian follicles: primordial, unilaminar primary, multilaminar primary, secondary, mature (Graafian). What hormones are secreted by the follicular cells? Identify the following follicular features: 1¾ oocyte, zona pellucida, membrana granulosum (granulosa cells), theca interna, theca externa. There is no corpus luteum in this section but you should find many corpora albicantes and atretic follicles.
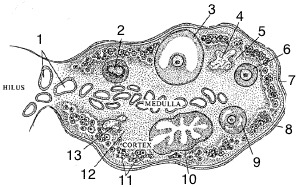
Section of a mature ovary: 1. Blood vessels; 2. Atretic follicle; 3. Mature follicle; 4. Corpus albicans; 5. Stroma; 6. Growing follicle; 7. Cuboidal epithelium; 8. Tunica albuginea; 9. Antrum of secondary follicle; 10. Corpus luteum; 11. Primordial follicles; 12. Stroma; 13. Corpus albicans